| [1]Battistella E,Varoni E,Cochis A,et al.Degradable polymers may improve dental practice J Appl Biomater Biomech. 2011;9(3):223-231.[2]Lee W,Debasitis JC, Lee VK,et al.Multi-layered culture of human skin fibroblasts and keratinocytes through three-dimensional freeform fabrication.Biomaterials. 2009;30(8):1587-1595.[3]Yang EK,Seo YK,Youn HH,et al.Tissue engineered artificial skin composed of dermis and epidermis. Artif Organs. 2000;24(1):7-17.[4]陈红.英国研究出3D打印人类眼角膜新材料[J].计算机与网络, 2018,44(12): 10.[5]Lee W,Lee V,Polio S,et al.On-demand three-dimensional freeform fabrication of multi-layered hydrogel scaffold with fluidic channels. Biotechnol Bioeng.2010;105(6):1178-1186.[6]Hribar KC,Soman P,Warner J,et al.Light-assisted direct-write of 3D functional biomaterials. Lab Chip.2013;14(2):268-275.[7]Yuichi N,Makoto N,Chizuka H,et al.Development of a three-dimensional bioprinter: construction of cell supporting structures using hydrogel and state-of-the-art inkjet technology.J Biomech Eng.2009;131(3):35001.[8]Christensen K,Xu C,Chai W,et al.Freeform inkjet printing of cellular structures with bifurcations.Biotechnol Bioeng.2015;112(5):1047-1055.[9]Xu C,Chai W,Huang Y,et al.Scaffold-free inkjet printing of three-dimensional zigzag cellular tubes. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2015; 109(12):3152-3160.[10]Ozbolat IT,Monika H.Current advances and future perspectives in extrusion-based bioprinting. Biomaterials.2016;76(37):321-343.[11]Zhang Y,Yu Y,Ozbolat IT.Direct Bioprinting of Vessel-Like Tubular Microfluidic Channels.J Nanotechnol Eng Med.2013;4(2):21001.[12]Massa S,Sakr MA,Seo J,et al. Bioprinted 3D vascularized tissue model for drug toxicity analysis. Biomicrofluidics.2017;11(4):44109.[13]Zhang Y,Yu Y,Chen H,et al.Characterization of printable cellular micro-fluidic channels for tissue engineering.Biofabrication.2013;5(2): 25004.[14]Luo Y,Lode A,Gelinsky M.Direct Plotting of Three‐Dimensional Hollow Fiber Scaffolds Based on Concentrated Alginate Pastes for Tissue Engineering. Adv Healthc Mater.2013;2(6):777-783.[15]Cheng Y,Zheng F,Lu J,et al.Bioinspired multicompartmental microfibers from microfluidics. Adv Mater.2014;26(30):5184-5190.[16]Gao Q,Liu Z,Lin Z,et al.3D Bioprinting of Vessel-like Structures with Multi-level Fluidic Channels.Acs Biomater Sci Eng.2017;3(3). DOI: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.6b00643[17]Onoe H,Okitsu T,Itou A, et al. Metre-long cell-laden microfibres exhibit tissue morphologies and functions.Nat Mater.2013;12(6):584.[18]Rowley JA,Madlambayan G,Mooney DJ.Alginate hydrogels as synthetic extracellular matrix materials.Biomaterials.1999;20(1):45-53.[19]Wang S, Zhang Y, Yin G, et al. Electrospun polylactide/silk fibroin– gelatin composite tubular scaffolds for small‐diameter tissue engineering blood vessels.J Appl Polym Sci. 2010;113(4): 2675-2682.[20]Wang SD,Zhang YZ,Yin GB,et al.Fabrication of a composite vascular scaffold using electrospinning technology.MaterSci Eng C.2010;30(5): 670-676.[21]Rodriguez MJ,Brown J,Giordano J,et al.Silk based bioinks for soft tissue reconstruction using 3-dimensional (3D) printing with in vitro and in vivo assessments. Biomaterials 2017;117:105-115.[22]Chawla S,Midha S,Sharma A,et al.Silk‐Based Bioinks for 3D Bioprinting. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018;7(8):e1701204.[23]Unger RE,Wolf M,Peters K,et al.Growth of human cells on a non-woven silk fibroin net: a potential for use in tissue engineering.Biomaterials. 2004;25(6):1069-1075.[24]Liu H,Xu GW,Wang YF,et al.Composite scaffolds of nano-hydroxyapatite and silk fibroin enhance mesenchymal stem cell-based bone regeneration via the interleukin 1 alpha autocrine/paracrine signaling loop.Biomaterials. 2015;49:103-112.[25]Zhou J, Cao C, Ma X, et al.In vitro and in vivo degradation behavior of aqueous-derived electrospun silk fibroin scaffolds.Polym Degrad Stabil. 2010;95(9):1679-1685.[26]Kweon HY, Yeo JH, Lee KG, et al. Effects of poloxamer on the gelation of silk sericin. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2000;21(18):1302-1305[27]Kimsey RB,Spielman A.Motility of Lyme disease spirochetes in fluids as viscous as the extracellular matrix.J Infect Dis.1990;162(5):1205-1208.[28]Zhao Y,Li Y,Mao S,et al. The influence of printing parameters on cell survival rate and printability in microextrusion-based 3D cell printing technology.Biofabrication.2015;7(4):45002.[29]Jia W,Gungor-Ozkerim PS,Zhang YS,et al.Direct 3D bioprinting of perfusable vascular constructs using a blend bioink.Biomaterials. 2016; 106:58-68.[30]王秀娟,张坤生,任云霞,等.海藻酸钠凝胶特性的研究[J].食品工业科技,2008, 29(2):259-262.[31]Wang L,Xu M,Zhang L,et al. Automated quantitative assessment of three-dimensional bioprinted hydrogel scaffolds using optical coherence tomography.Biomed Opt Express.2016;7(3):894-910.[32]Wang L,Xu ME, Luo L,et al.Iterative feedback bio-printing-derived cell-laden hydrogel scaffolds with optimal geometrical fidelity and cellular controllability.Sci Rep.2018;8(1):2802.[33]罗会涛,赵婧,范兴平,等.不同类型多孔结构生物材料支架制备及其性能优化[J].中国材料进展, 2012,31(5):30-39.[34]Armstrong JP,Burke M, Carter BM, et al.3D Bioprinting Using a Templated Porous Bioink.Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(14):1724-1730.[35]Kantlehner M,Schaffner P,Finsinger D,et al.Surface Coating with Cyclic RGD Peptides Stimulates Osteoblast Adhesion and Proliferation as well as Bone Formation.Chembiochem.2015;1(2):107-114.[36]Ishaug-Riley SL,Crane-Kruger GM,Yaszemski MJ,et al. Three-dimensional culture of rat calvarial osteoblasts in porous biodegradable polymers.Biomaterials. 1998;19(15):1405.[37]Mikos AG,Lyman MD,Freed LE,et al.Wetting of poly(L-lactic acid) and poly(DL-lactic-co-glycolic acid) foams for tissue culture.Biomaterials. 1994;15(1):55-58.[38]Gao Q,He Y,Fu JZ,et al.Coaxial nozzle-assisted 3D bioprinting with built-in microchannels for nutrients delivery.Biomaterials. 2015;61: 203-215. |
.jpg)
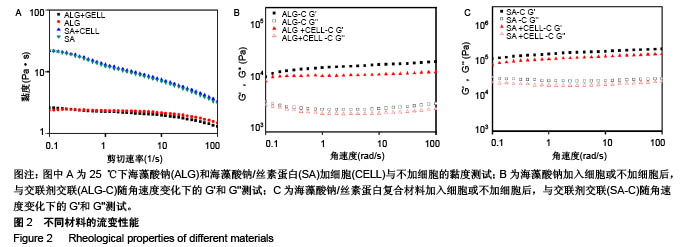


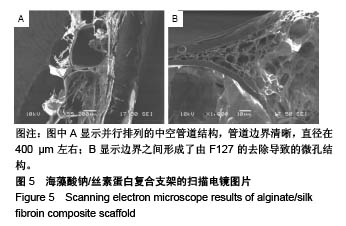
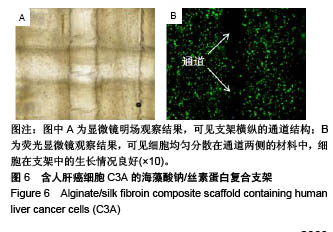
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)